

patients worldwide.
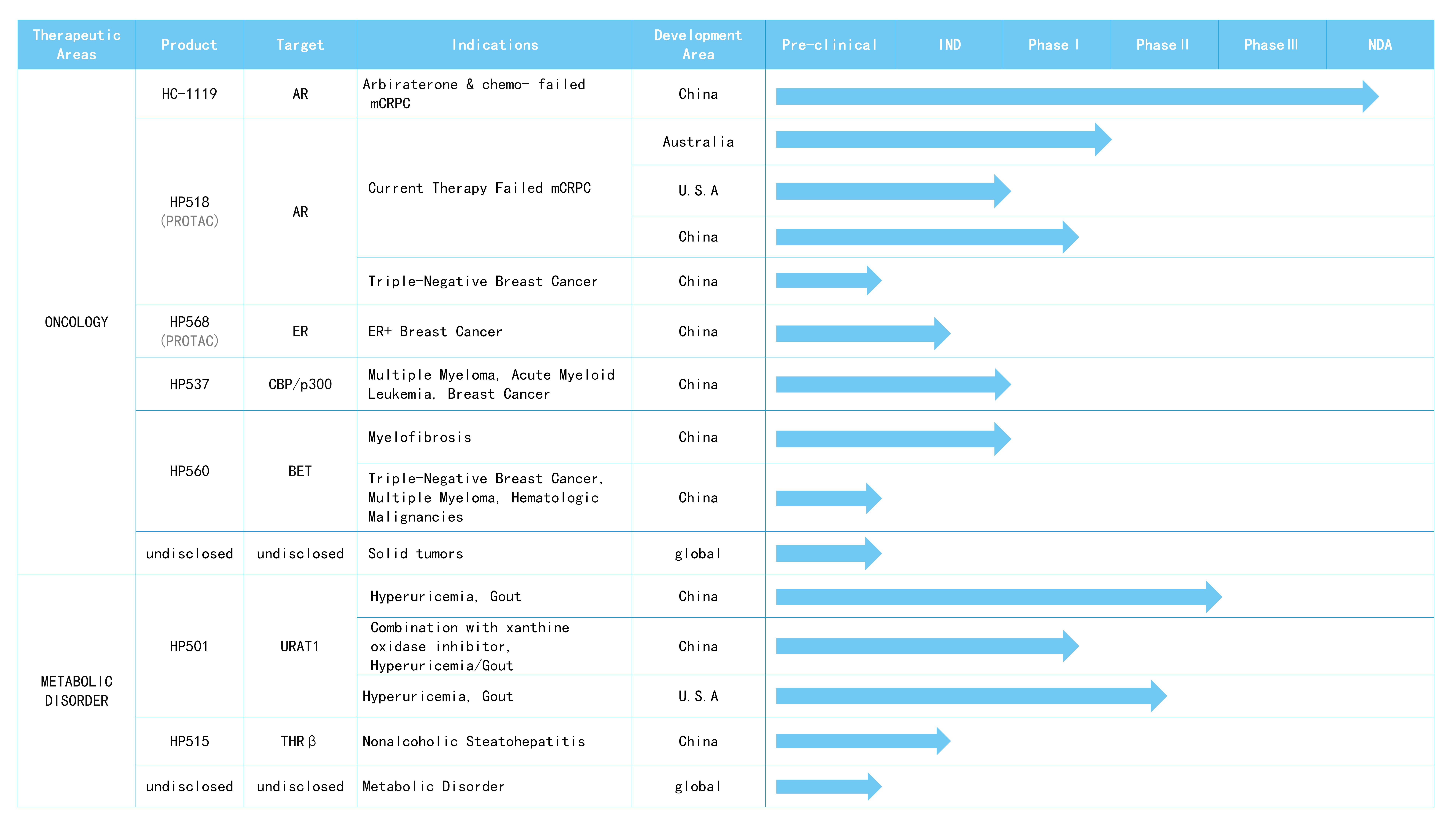
HC-1119 is the deuterated compound of enzalutamide, which is a second-generation AR antagonist. Compared to enzalutamide, HC-1119 has lower metabolic rate, higher plasma exposure, and lower brain exposure at equivalent doses in preclinical model. HC-1119 has the potential to be safer and to be used at a lower clinical dose. HC-1119 program has been adopted into National Major Projects of “Significant New Drugs Creation”. Two phase-III clinical trials are being carried out in China and globally,the NDA application of HC-1119 was accepted by NMPA in November 2023.
The excessive purine intaking, increased synthesis and decreased excretion of uric acid are the main causes for hyperuricemia. Uric acid is excreted by kidney (70%), skin (15%) and intestine (15%). Therefore, impaired kidney function directly leads to hyperuricemia. Long-term hyperuricemia would induce a build-up of uric acid crystals under the skin and around the joints, which eventually results in gout.
Drugs for the treatment of hyperuricemia can be divided into three types, xanthine oxidase inhibitor, urate oxidases and URAT1 inhibitors. 40%-60% hyperuricemia patients treated with xanthine oxidase inhibitors alone cannot achieve desirable serum uric acid concentration. Using urate oxidases may result in drug resistance. As a URAT1 inhibitor, benzbromarone may cause fulminant hepatitis, and was banned in Europe and U.S. Another URAT1 inhibitors, lesinurad, was removed from U.S. and Europe in 2019 and 2020 respectively because of the risk of increasing serum creatinine and renal injury. Hence, it is necessary to develop new drugs that are safer and more effective for the treatment of hyperuricemia/gout.
In the early strategy of Hinova's URAT1 development, we evaluated hepatorenal toxicity of compound candidates. While during preclinical toxicology study, anthropoid primates was incorporated for safety evaluation. Furthermore, we decrease the potential side effects by formulation optimizations. At present phase II clinical trial of HP501.
Patient Recruitment
HP518 is an oral PROTAC drug, with the potential to solve the drug resistance to prostate cancer due to AR variation. HP518 demonstrates good oral exposure and bioavailability in animal model. HP518 has high activity of degrading wild type AR and variant AR resistant to enzalutamide, high selectivity to AR, and excellent anticancer activity of AR-dependent prostate cancer cells. It also shows obvious effect on prostate cancer animal model. At present HP518 is in Phase I/II clinical study.



